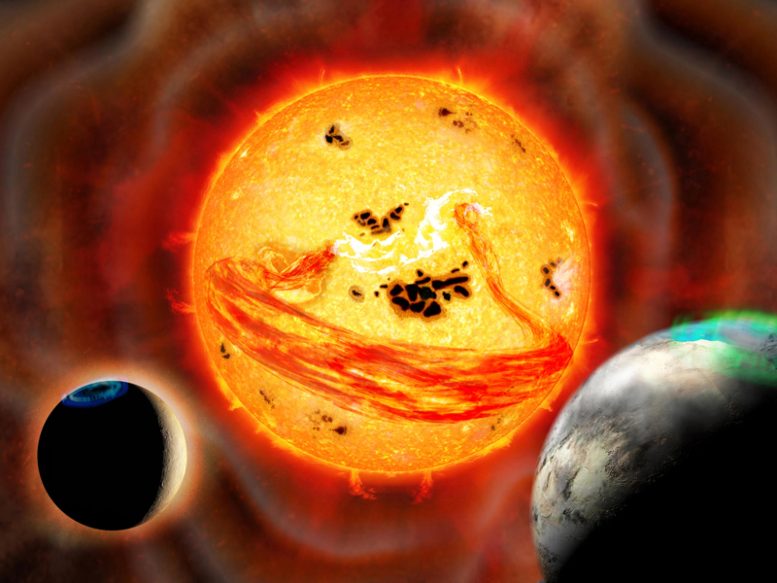
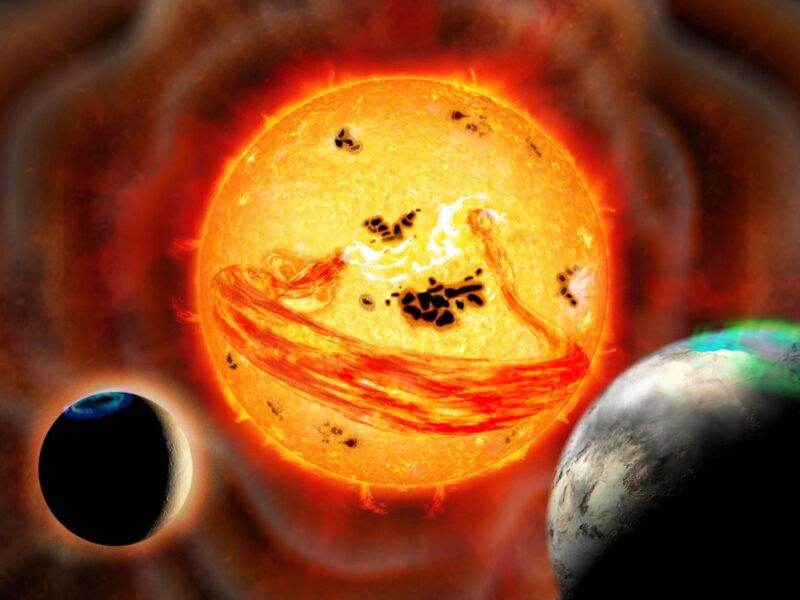
Représentation artistique de l’étoile EK Draconis qui produit une éjection de masse coronale alors que deux planètes sont en orbite. Crédit : Observatoire national d’astronomie du Japon
Dans la recherche de planètes extrasolaires “potentiellement habitables”, l’une des principales choses que les scientifiques examinent est l’activité stellaire. Alors que les étoiles comme la nôtre, une naine jaune de type G (G2V), sont considérées comme stables dans le temps, d’autres classes sont variables et sujettes à des éruptions – en particulier les naines rouges de type M. Même si une étoile possède plusieurs planètes en orbite dans sa zone habitable (ZH), la tendance à l’éruption périodique pourrait rendre ces planètes complètement inhabitables.
Selon une nouvelle étude, les étoiles comme la nôtre ne sont peut-être pas aussi stables qu’on le pensait. En observant EK Draconis, une naine jaune G1.5V située à 110,71 années-lumière, une équipe internationale d’astronomes a été témoin d’une éjection massive de masse coronale qui a éclipsé tout ce que nous avons jamais vu dans notre système solaire. Ces observations suggèrent que ces éjections peuvent s’aggraver avec le temps, ce qui pourrait être un avertissement pour la vie sur Terre.
L’étude, qui est apparue dans le journal Nature Astronomya été menée par le Dr Kosuke Namekata, chercheur à l’Université de Kyoto, à l’Observatoire astronomique national du Japon (NAOJ) et à l’Observatoire solaire national (NSO). Il a été rejoint par des chercheurs du Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) de CU Boulder, de l’Observatoire astronomique de Nishi-Harima (NHAO), de l’Institut de technologie de Tokyo, de la Graduate School of Advanced Integrated Studies in Human Survivability et de plusieurs universités.
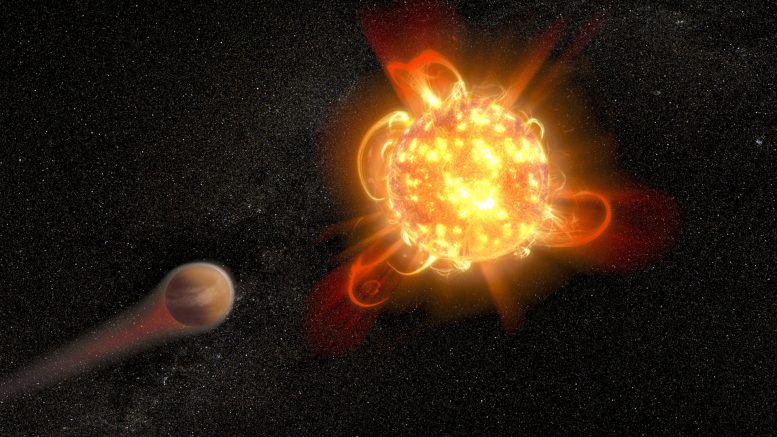

Les éruptions stellaires pourraient menacer la vie sur les planètes naines rouges. Crédits : NASA, ESA et D. Player (STScI)
Leur étude explore un phénomène stellaire connu sous le nom d'”éjection de masse coronale” (CME), alias tempête solaire. Ces éjections, qui se produisent régulièrement avec notre Soleil, accompagnent souvent une éruption stellaire (ou un éclat soudain et brillant de radiation). Lorsqu’elles se produisent, les CME envoient des nuages de particules chargées extrêmement chaudes (aka. plasma) at extremely high velocities into space. While Earth is protected from charged particles by its planetary magnetic field, a CME could cause significant damage if it hit Earth head-on.
Astronauts in orbit would be exposed to lethal radiation levels, satellites would be disabled, and Earth-based infrastructure (like electrical grids) would be knocked out. Earth has experienced several powerful geomagnetic storms over time, the most well-known example of which was the Carrington Event in 1859. Several such events have occurred in Earth’s history and are usually several thousand years apart.
While studying EK Draconis, the research team observed evidence that superflares may become worse for Sun-like stars over time. As co-author Yuta Notsu (LASP) explained in a recent CU Boulder Today press release:
“Coronal mass ejections can have a serious impact on Earth and human society. This kind of big mass ejection could, theoretically, also occur on our sun. This observation may help us to better understand how similar events may have affected Earth and even Mars over billions of years.”
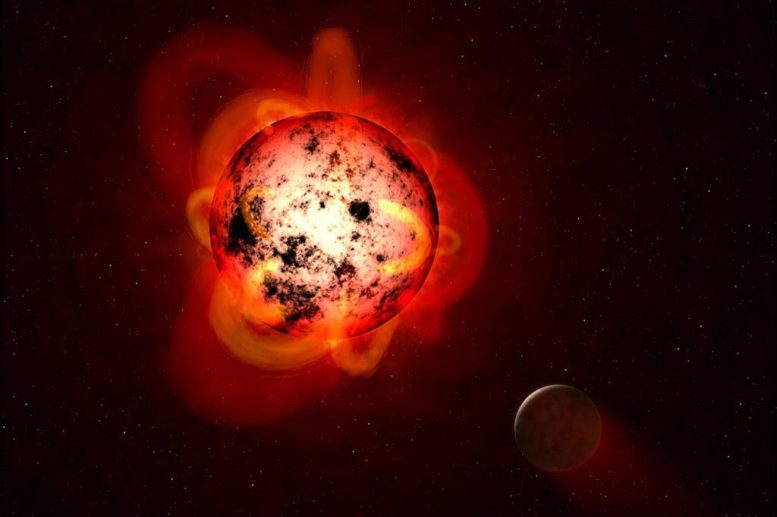

An illustration of a flaring red dwarf star orbited by an exoplanet. Credit: NASA/ESA/G. Bacon (STScI)
The research builds on previous research by co-author Yuta Notsu, who was joined by many of the researchers who conducted this latest study. They showed how young Sun-like stars experience frequent superflares that are tens to hundreds of times more powerful than solar flares. The Sun has been known to experience superflares, which appear to happen once every several thousand years. This raised the question: could a superflare also lead to an equally massive “super coronal mass ejection”?
While astronomers have speculated about a possible relationship between these two phenomena, no evidence has been found for it before. To investigate this possibility, Namekata, Notsu, and their colleagues decided to study EK Draconis, which is similar to our Sun in terms of size and mass but is significantly young by comparison (100 million years old compared to our Sun, which is 4.6 billion years old).
For the sake of their observations, Namekata, Notsu, and their colleagues used NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and Kyoto University’s SEIMEI Telescope to observe EK Draconis (which looks like a young version of the Sun) for 32 nights in the winter and spring 2020. On April 5th, 2020, the team observed EK Draconis erupt into a superflare, followed 30 minutes later by a massive ejection of super-hot plasma. Said Notsu:
“This kind of big mass ejection could, theoretically, also occur on our Sun. This observation may help us to better understand how similar events may have affected Earth and even Mars over billions of years. It’s what our Sun looked like 4.5 billion years ago.”
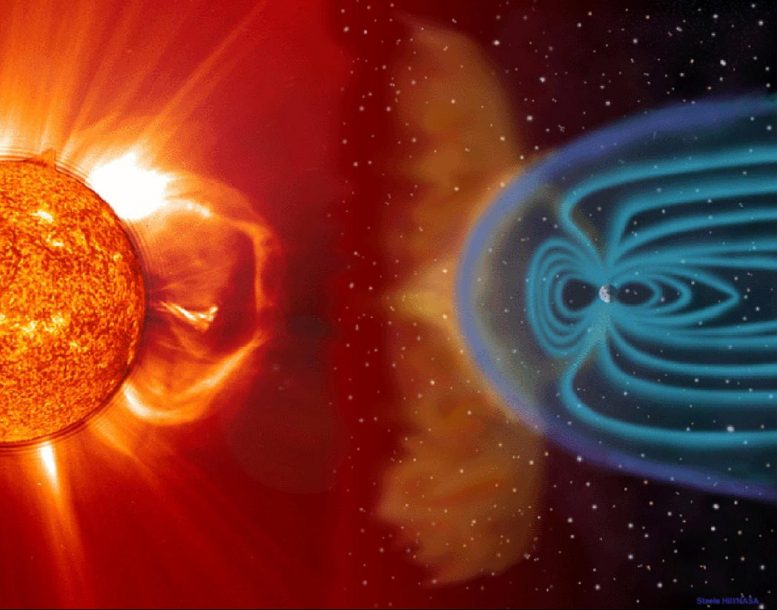
This visualization depicts what a coronal mass ejection might look like as it interacts with the interplanetary medium and magnetic forces. Credit: Magnetosphere: NASA, the Sun: ESA/NASA – SOHO
The team was only able to observe the first step in the ejection’s life – the “filament eruption” phase – but were still able to obtain mass and velocity estimates. According to their study, the cloud was more than ten times as large as the most powerful CME ever recorded from a Sun-like star and had a top speed of roughly 1.6 million km (1 million mph). The event could indicate just how dangerous space weather can be.
If such an eruption were to occur from our Sun, it would have the potential to strip Earth’s atmosphere and render our planet largely sterile. While their findings indicate that the Sun could be capable of such violent extremes, they also suggest that superflares and super CMEs are probably rare for stars as old as the Sun. But as Notsu explained, super CMEs may have been much more common billions of years ago when our Solar System was still forming.
Super CMEs, in other words, could have played a role in the evolution of planets like Earth and Mars, which includes how one gave rise to life while the other did not. “The atmosphere of present-day Mars is very thin compared to Earth’s,” he said. “In the past, we think Mars had a much thicker atmosphere. Coronal mass ejections may help us to understand what happened to the planet over billions of years.”
This same knowledge could come in handy if and when future generations begin to live on Mars. Protecting the atmosphere from solar activity (including CMEs) will allow the atmosphere to replenish over time, making the planet warmer, wetter, and altogether more liveable!
Originally published on Universe Today.
For more on this research, see A Sun-Like Star May Hold Dire Warnings for Life on Earth.
Reference: “Probable detection of an eruptive filament from a superflare on a solar-type star” by Kosuke Namekata, Hiroyuki Maehara, Satoshi Honda, Yuta Notsu, Soshi Okamoto, Jun Takahashi, Masaki Takayama, Tomohito Ohshima, Tomoki Saito, Noriyuki Katoh, Miyako Tozuka, Katsuhiro L. Murata, Futa Ogawa, Masafumi Niwano, Ryo Adachi, Motoki Oeda, Kazuki Shiraishi, Keisuke Isogai, Daikichi Seki, Takako T. Ishii, Kiyoshi Ichimoto, Daisaku Nogami and Kazunari Shibata, 9 December 2021, Nature Astronomy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41550-021-01532-8



