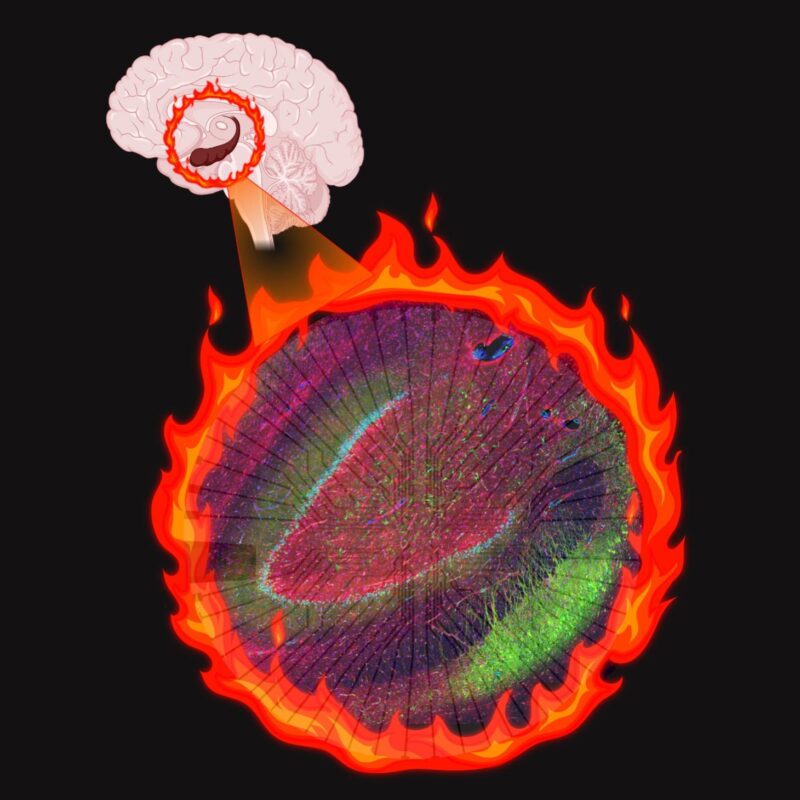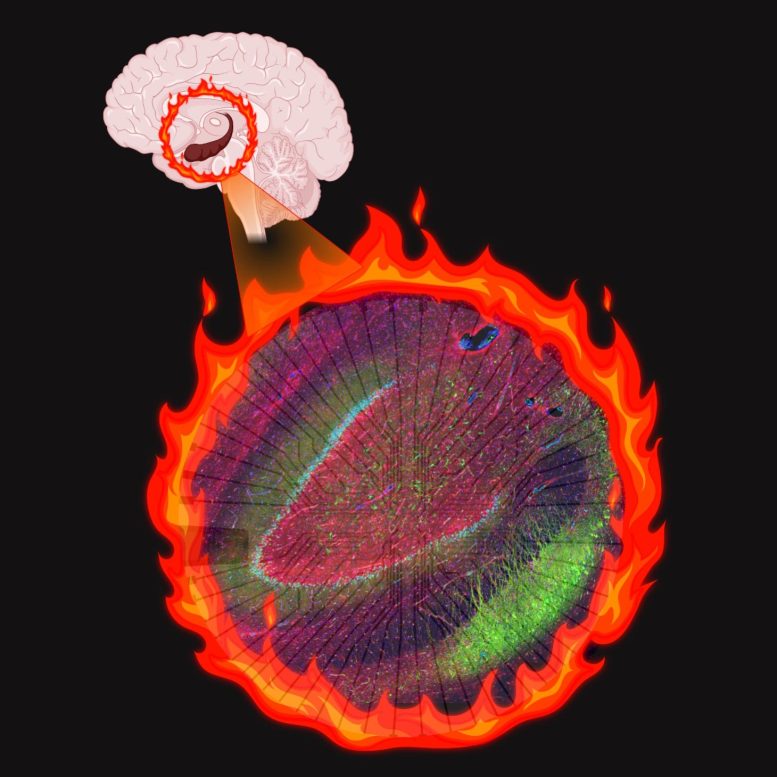
Les cellules altérées créent un “feu” électrique chez les patients épileptiques. Crédit : Illustration BioRender par Aswathy Ammothumkandy/Bonaguidi Lab/USC Stem Cell.
Au fil des années, tout le monde perd quelques cellules cérébrales. Une étude menée par des scientifiques de Fondée en 1880, la University of Southern California> ; est l’une des principales universités de recherche privées du monde. Elle est située au cœur de Los Angeles.
;” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{” attribute=””>USC Stem Cell and the USC Neurorestoration Center presents evidence that adults can replenish at least some of what they’ve lost by generating new brain cells, and that this process is dramatically altered in patients with long-term epilepsy. The findings are published in Nature Neuroscience.
“Our study is the first to detail the presence of newborn neurons and an immature version of a related cell type, known as astroglia, in patients with epilepsy,” said Michael Bonaguidi, an assistant professor of stem cell biology and regenerative medicine, gerontology, and biomedical engineering at USC. “Our findings furnish surprising new insights into how immature astroglia might contribute to epilepsy—opening an unexplored avenue toward the development of new anti-seizure medications for millions of people.”
First author Aswathy Ammothumkandy, who is a postdoctoral fellow in the Bonaguidi Lab, and her colleagues collaborated with USC neurosurgeons Charles Liu and Jonathan Russin, who often treat patients with seizures that can’t be controlled with medication. Drug resistance is particularly common with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy, or MTLE, and affects one-third of all patients with this form of the disease. As a result, some patients need to undergo surgery to remove the section of the brain, the hippocampus, that causes their seizures.
“Many patients bravely and generously donate their surgical specimens for research to advance our understanding of epilepsy and to develop new and better therapies,” said Russin, an assistant professor of neurological surgery, and associate director of the USC Neurorestoration Center. “These patients know better than anyone the trade-offs involved in the current treatment options, which often either don’t provide adequate seizure control, or carry very serious cognitive side effects.”
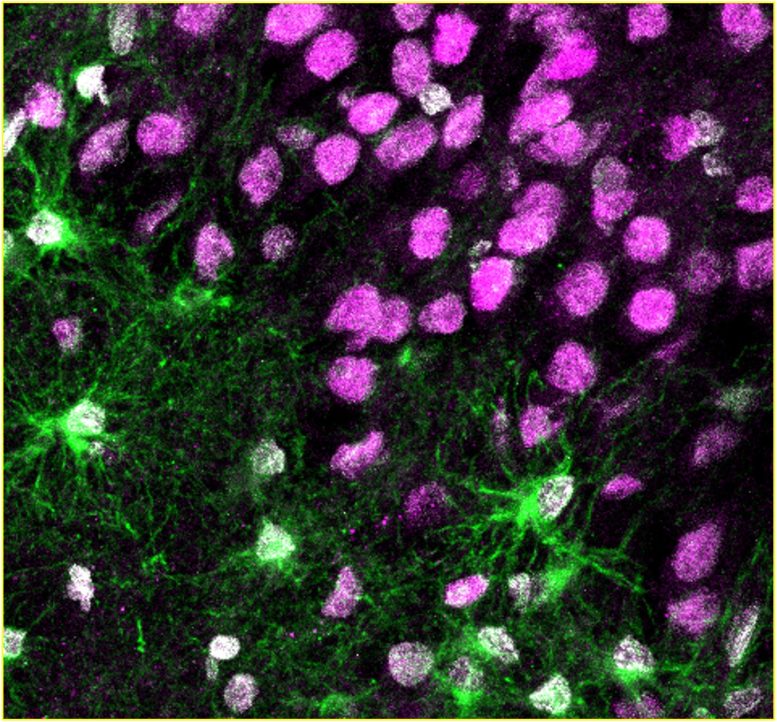
Newborn astroglia (green) in brain tissue from human epilepsy patients. Credit: Image by Aswathy Ammothumkandy/Bonaguidi Lab/USC Stem Cell
The surgical specimens afforded a unique opportunity for the researchers to study living brain tissue from patients with epilepsy, and to compare its microscopic anatomy with post-mortem samples from people with no known neurological disease.
In the samples from people both with and without epilepsy, the scientists observed newborn neurons, adding compelling new evidence to the ongoing scientific debate about whether adults retain the ability to generate these cells. In the surgical specimens, the longer the patients had experienced seizures, the scarcer these newborn neurons became. More surprisingly, the surgical specimens contained a persistent population of immature astroglia that were not observed in the disease-free samples.
Because the brain tissue in the surgical specimens was still alive, the scientists could also use it to grow stem cells in the laboratory and test their ability to form newborn neurons and immature astrocytes. In these experiments, a longer disease duration reduced the ability to form newborn neurons and increased the production of immature astroglia, consistent with the team’s direct observations of the surgical specimens.
The team also studied electrical activity related to seizures. They found suspicious correlations between where electrical activity was localized within the surgical samples, and the location and behavior of the astroglia.
“Normally, astroglia are considered to be supporting cells, because their job is to create an environment where neurons can thrive,” said Ammothumkandy. “But in patients who have lived for many years with epilepsy, it might be immature astroglia that are contributing to both initiating and modulating chronic seizures.”
If this is the case, then immature astroglia could be an effective cell type to target by developing an entirely new class of anti-seizure medications.
“Currently available seizure medications tend to target neurons, so medications that act on immature astroglia could greatly expand the options for our patients,” said Liu, a professor of neurological surgery, neurology, and biomedical engineering, director of the USC Neurorestoration Center, and director of the USC Epilepsy Care Consortium. “A new class of drugs could combine with current medical and surgical strategies to control seizures without aggressive surgical removal of parts of the brain that can be critically important for learning, memory and emotional regulation.”
Reference: “Altered adult neurogenesis and gliogenesis in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy” 5 April 2022, Nature Neuroscience.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-022-01044-2
Bonaguidi, Liu, and Russin originally kicked off the project with pilot funding from an Eli and Edythe Broad Innovation Award, which supports faculty pursuing research collaborations related to stem cells. The study brought together clinicians, scientists and engineers from across the Keck School of Medicine of USC—including at the Eli and Edythe Broad Center for Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at USC, the USC Neurorestoration Center, and the Zilkha Neurogenetic—the USC Epilepsy Care Consortium, the USC Viterbi School of Engineering, and the USC Davis School of Gerontology, as well as other universities and medical centers.
About the study
Additional co-authors include: Kristine Ravina, Victoria Wolseley, Pen-Ning Yu, Luis Corona, Naibo Zhang, George Nune, Laura Kalayjian, Brian Lee, Dong Song, Theodore W. Berger, Christianne Heck, and Robert H. Chow from USC; Jason A. D. Smith from USC and the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center; Alexandria N. Tartt from the New York State Psychiatric Institute; J. John Mann, Victoria Arango, and Maura Boldrini from the New York State Psychiatric Institute and Columbia University; and Gorazd B. Rosoklija and Andrew J. Dwork from the New York State Psychiatric Institute, Columbia University, and the Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts.
Sixty percent of the funding for this project came from federal grants from the National Institutes of Health (grants R00NS089013, R56AG064077, MH83862, NS090415, MH94888, U01MH098937, MH64168, MH098786, MH090964), and the remaining 40 percent was from non-federal sources including the Donald E. and Delia B. Baxter Foundation, the L.K. Whittier Foundation, The Eli and Edythe Broad Foundation, the USC Neurorestoration Center, the Rudi Schulte Research Institute, the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (grant SRG-0-129-12), the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation (Independent Investigator Grant 56388), the New York Stem Cell Initiative (grant C029157, C023054), the Dr. Brigitt Rok-Potamkin’s Foundation, the Morris Stroud III Center for Study of Quality of Life in Health and Aging, and the American Epilepsy Society.
About the Keck School of Medicine of USC
Founded in 1885, the Keck School of Medicine of USC is one of the nation’s leading medical institutions, known for innovative patient care, scientific discovery, education and community service. Medical and graduate students work closely with world-renowned faculty and receive hands-on training in one of the nation’s most diverse communities. They participate in cutting-edge research as they develop into tomorrow’s health leaders. The Keck School faculty are key participants in training of 1200 resident physicians across 70 specialty and subspecialty programs, thus playing a major role in the education of physicians practicing in Southern California.