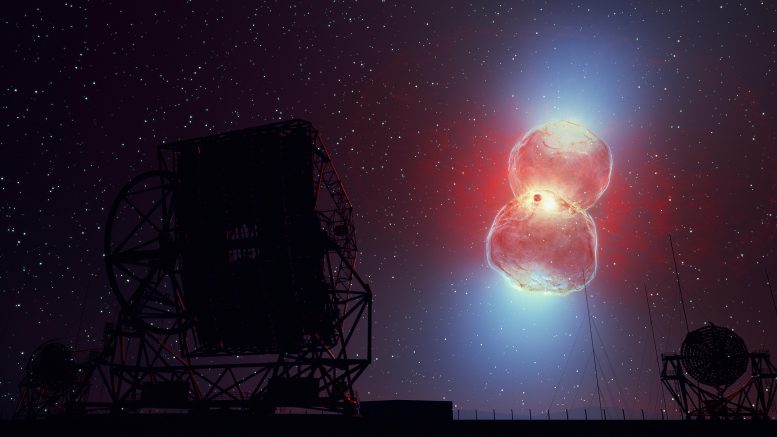
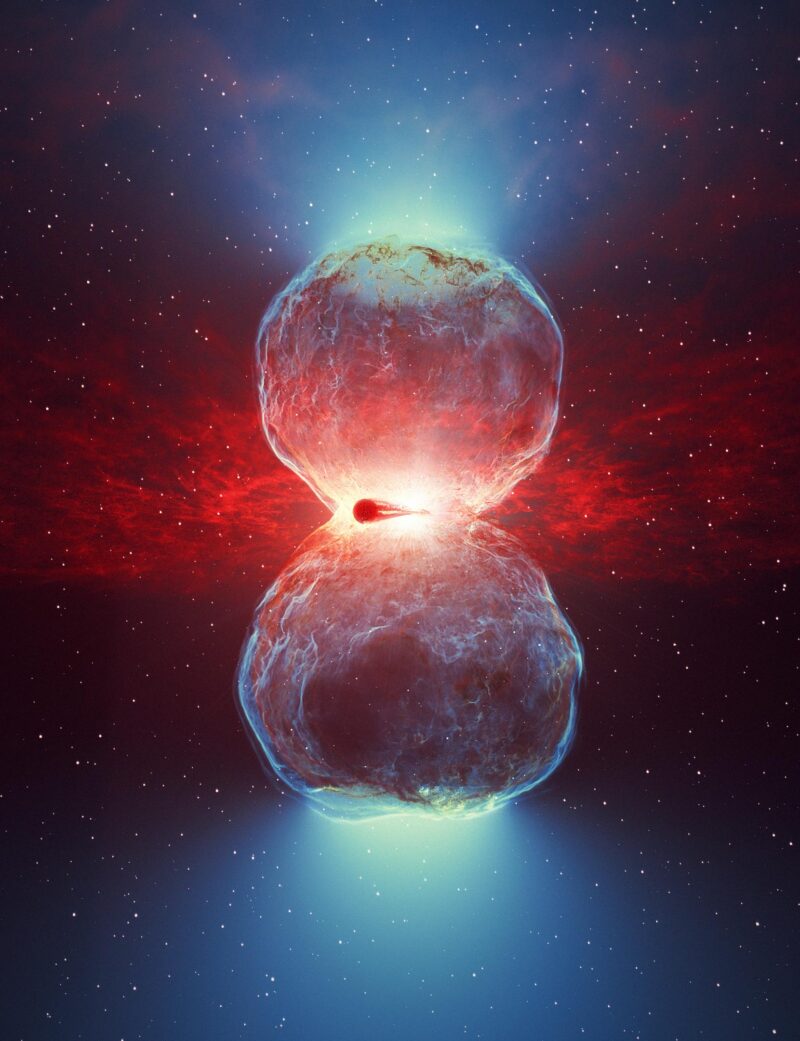
Les ondes de choc rapides forment une forme de sablier lors de leur expansion, dans laquelle des rayons gamma sont produits. Cette émission de rayons gamma est ensuite détectée par les télescopes H.E.S.S. (au premier plan). Crédit : DESY/H.E.S.S., Science Communication Lab.
L’observatoire de rayons gamma H.E.S.S. révèle un processus d’accélération de particules cosmiques avec des détails sans précédent.
A l’aide de télescopes spéciaux, des chercheurs ont observé un accélérateur de particules cosmiques comme jamais auparavant. Les observations réalisées avec l’observatoire de rayons gamma H.E.S.S. en Namibie montrent pour la première fois le déroulement d’un processus d’accélération dans un processus stellaire appelé nova, qui comprend de puissantes éruptions à la surface d’une white dwarf. A nova creates a shock wave that tears through the surrounding medium, pulling particles with it and accelerating them to extreme energies. Surprisingly, the nova “RS Ophiuchi” seems to cause particles to accelerate at speeds reaching the theoretical limit, corresponding to ideal conditions. The research has been published in the journal Science.
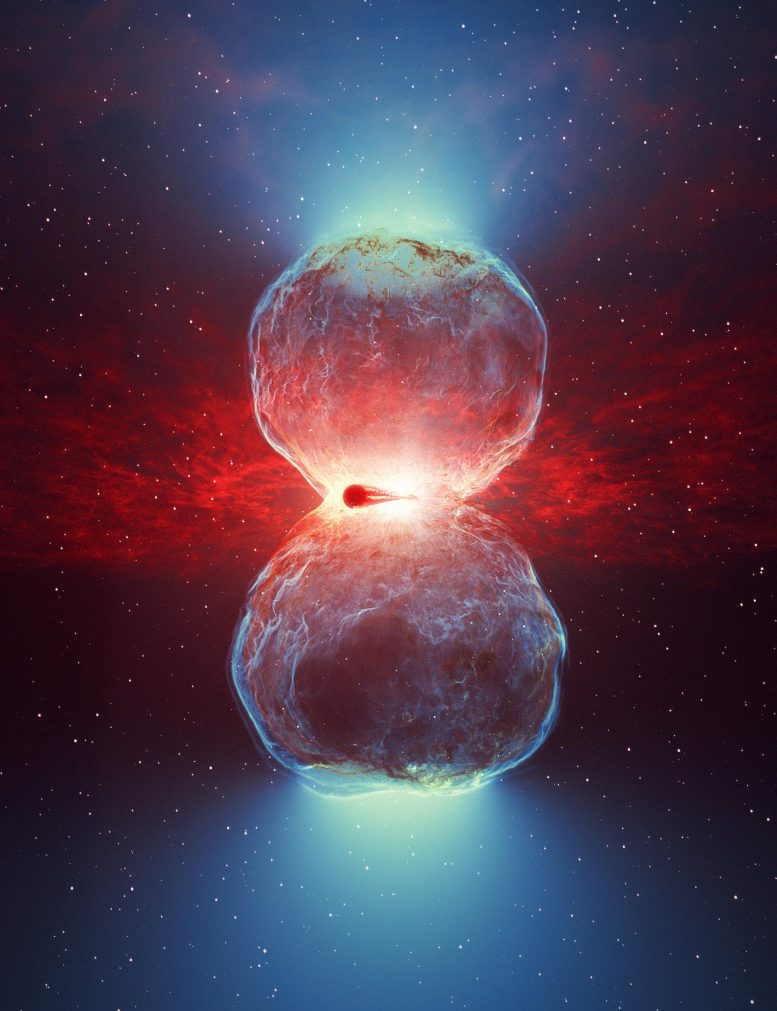

Material ejected from the surface of the white dwarf generates shockwaves that rapidly expand, forming an hourglass shape. Particles are accelerated at these shock fronts, which collide with the dense wind of the red giant star to produce very-high-energy gamma-ray photons. Credit: DESY/H.E.S.S., Science Communication Lab
White dwarves are burned-out old stars that have collapsed in on themselves and develop into extremely compact objects. Novae events occur, for example, when a white dwarf is in a binary system with a large star, and the white dwarf gathers material from its more massive companion due to its gravity. Once the gathered material goes over a critical level, it spurs a thermonuclear explosion on the surface of the white dwarf. Some novae are known to repeat. RS Ophiuchi is one of these recurrent novae; there is an explosion on its surface every 15 to 20 years. “The stars forming the system are at approximately the same distance from each other as the Earth and the Sun,” explains Alison Mitchell, researcher at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg and principal investigator of the H.E.S.S Nova program. “When the nova exploded in August 2021, the H.E.S.S. telescopes allowed us to observe a galactic explosion in very-high-energy gamma rays for the first time,” she continues.
The research group observed that the particles were accelerated to energies several hundreds of times higher than previously observed in novae. Additionally, the energy released as a result of the explosion was transformed extremely efficiently into accelerated protons and heavy nuclei, such that the particle acceleration reached the maximum speeds calculated in theoretical models. According to Ruslan Konno, one of the lead authors of the study and a doctoral candidate at DESY in Zeuthen, “The observation that the theoretical limit for particle acceleration can actually be reached in genuine cosmic shock waves has enormous implications for astrophysics. It suggests that the acceleration process could be just as efficient in their much more extreme relatives, supernovae.”
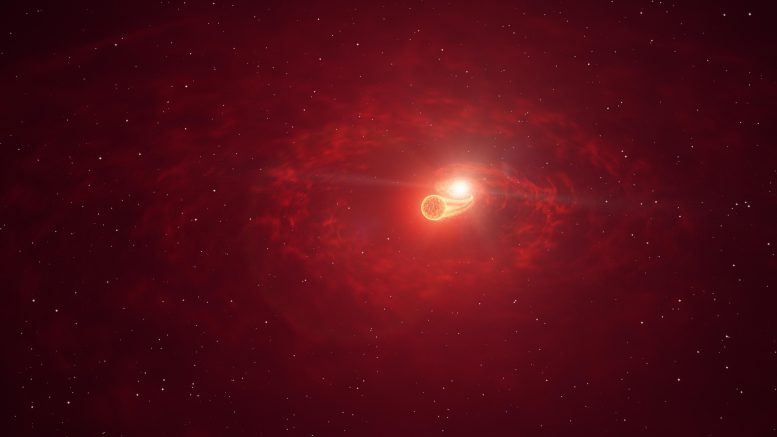

Artist’s impression of the RS Ophiuchi binary star system, which is comprised of a white dwarf (background) and red giant that orbit each other. Material from the red giant is continually accreted by the companion star. Credit: DESY/H.E.S.S., Science Communication Lab
During the eruption of RS Ophiuchi, the researchers were able for the first time to follow the development of the nova in real time, allowing them to observe and study cosmic particle acceleration as if they were watching a film. The researchers were able to measure high-energy gamma rays up to one month after the explosion. “This is the first time we have ever been able to carry out observations like this, and it will allow us to gain even more accurate future insights into how cosmic explosions work,” explains Dmitry Khangulyan, a theoretical astrophysicist at Rikkyo University in Tokyo, Japan. “We may, for example, discover that novae contribute to the ever-present sea of cosmic rays and therefore have a considerable effect on the dynamics of their immediate surroundings.” Cosmic rays are immense showers of energetic subatomic particles that come from every direction in space at the same time, and which have an unclear exact origin.
Specific telescopes were required for these measurements. The H.E.S.S. facility (which stands for High Energy Stereoscopic System) in Namibia consists of five Cherenkov telescopes that are used to investigate gamma rays from space. A new, highly sensitive state-of-the-art camera – known as FlashCam – was recently installed in the largest telescope. The FlashCam design is currently being further developed for the next generation gamma-ray observatory, the Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA). “The new camera has been in use since late 2019, and this measurement shows just how much potential the latest generation of cameras has,” explains Simon Steinmaßl, a doctoral candidate at the Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics in Heidelberg, who was involved in analyzing the camera data.
The telescopes were pointed towards the nova at very short notice after amateur astronomers first reported the nova to the astrophysics community. The success of the observation was due in no small part to the rapid reaction of the researchers and the wider astronomical community, paving the way for extensive subsequent observations. H.E.S.S. Director Stefan Wagner, a professor at the regional observatory in Heidelberg, explains, “Over the next few years, research using the CTA telescopes will show whether this type of nova is special.” In addition, researchers now have a clearer idea of what to look for. This gives rise to a number of new possibilities for gaining a better understanding and being better able to explain events linked to novae. “This measurement is a further success in gamma-ray astronomy and an encouraging sign that we will be able to study many more cosmic explosions with H.E.S.S. and gamma-ray telescopes of the future.”
Reference: “Time-resolved hadronic particle acceleration in the recurrent nova RS Ophiuchi” by H.E.S.S. Collaboration, 10 March 2022, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.abn0567
About H.E.S.S.
The High Energy Stereoscopy System (H.E.S.S.) is an array of five imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes for studying cosmic gamma rays. The observatory is operated through an international collaboration. The telescopes are located in Namibia, near the Gamsberg mountain, in a region known for its excellent optical properties. Four H.E.S.S. telescopes went into operation in 2002/2003, the much larger fifth telescope known as H.E.S.S. II is operational since July 2012 and extends the energy coverage towards lower energies, as well as further improving sensitivity. More than 230 researchers from 41 institutes in 15 different countries are involved in H.E.S.S.