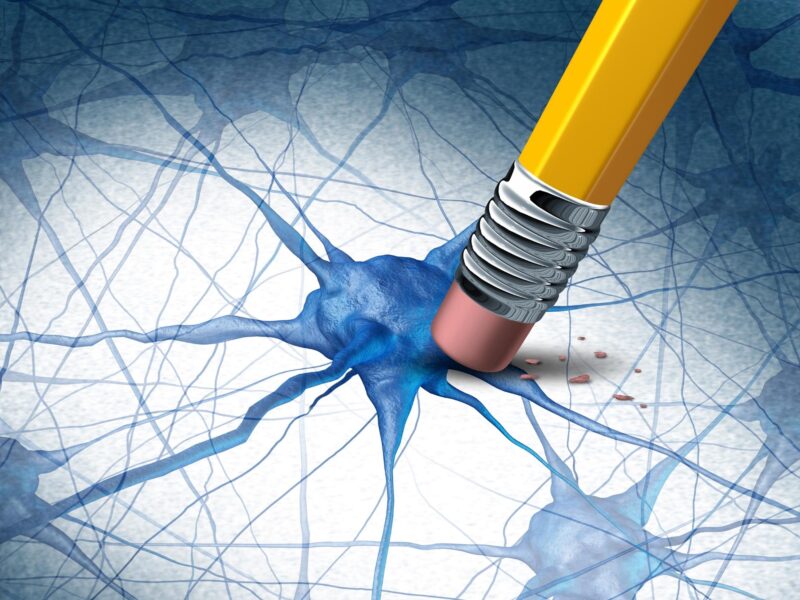
Selon une nouvelle analyse, des chercheurs affirment qu’il existe de “bonnes preuves” que les médicaments noradrénergiques utilisés pour traiter le trouble déficitaire de l’attention avec hyperactivité pourraient également traiter avec succès des aspects clés de la maladie d’Alzheimer.
Les chercheurs disent que les essais cliniques des médicaments ‘noradrénergiques’ sont maintenant justifiés.
Selon une nouvelle analyse des données regroupées des recherches disponibles, il existe de “bonnes preuves” que les médicaments utilisés pour traiter le trouble déficitaire de l’attention avec hyperactivité (ADHD) might also successfully treat key aspects of Alzheimer’s disease. This analysis was published on July 5, 2022, in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
The findings mean clinical trials of noradrenergic drugs, which include antidepressants and medicines to treat high blood pressure and ADHD, are now warranted, according to the researchers.
Noradrenergic drugs target the neurotransmitter noradrenaline, also known as norepinephrine, which is secreted by a network of specialized noradrenergic neurons.
Noradrenaline, also called norepinephrine, is a chemical made by some nerve cells and in the adrenal gland. It can function as both a neurotransmitter (a chemical messenger used by nerve cells) and a hormone (a chemical that travels in the blood and controls the actions of other cells or organs). Norepinephrine is released by the adrenal gland in response to stress and low blood pressure.
This network is critical for arousal and many cognitive processes, including attention, memory, learning, readiness for action, and suppression of inappropriate behaviors.
Noradrenergic disruption occurs early in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to the condition’s characteristic cognitive and neuropsychiatric symptoms, indicating that the noradrenergic system would be a viable target for drug treatment.
Therefore, the scientists looked for clinical trials published between 1980 and 2021 in which noradrenergic drugs, such as methylphenidate, atomoxetine, and guanfacine, had been used to potentially improve cognitive and/or neuropsychiatric symptoms in people with neurodegenerative disease.
A total of 19 randomized controlled trials were included, focusing on Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment, involving 1811 patients: six of these trials were judged to be ’good’ quality, seven as ’fair’, and six as ’poor’.
The results of 10 of these trials, involving 1300 patients, were pooled for global cognition—orientation/attention, memory, verbal fluency, language, and visuospatial ability.
This showed a small, but significant, positive effect of noradrenergic drugs on overall cognition, as measured by the Mini-Mental State Exam or the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale.
The results of 8 clinical trials, involving 425 patients, were then pooled for behavior and neuropsychiatric symptoms, agitation, and apathy. And this showed a large positive effect of noradrenergic drugs on apathy, even after removing outliers to account for differences in trial design and intended outcomes.
“Repurposing of established noradrenergic drugs is most likely to offer effective treatment in Alzheimer’s disease for general cognition and apathy,” say the researchers.
They add: “There is a strong rationale for further, targeted clinical trials of noradrenergic treatments in Alzheimer’s disease.”
But several factors need to be considered first, they caution. These include appropriate targeting of particular groups of patients and understanding the dose effects of individual drugs and their interactions with other treatments to minimize the cons and maximize the pros of noradrenergic drugs, they say.
Reference: “Cognitive and neuropsychiatric effects of noradrenergic treatment in Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis” by Michael C B David, Martina Del Giovane, Kathy Y Liu, Benjamin Gostick, James Benedict Rowe, Imafidon Oboh, Robert Howard and Paresh A Malhotra, 5 July 2022, Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
DOI: