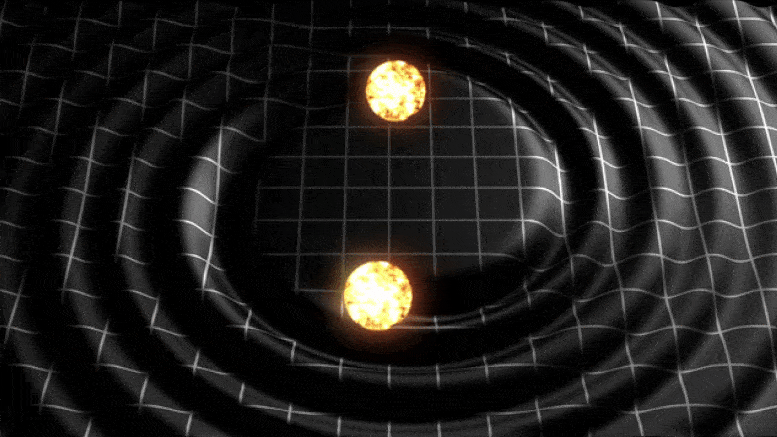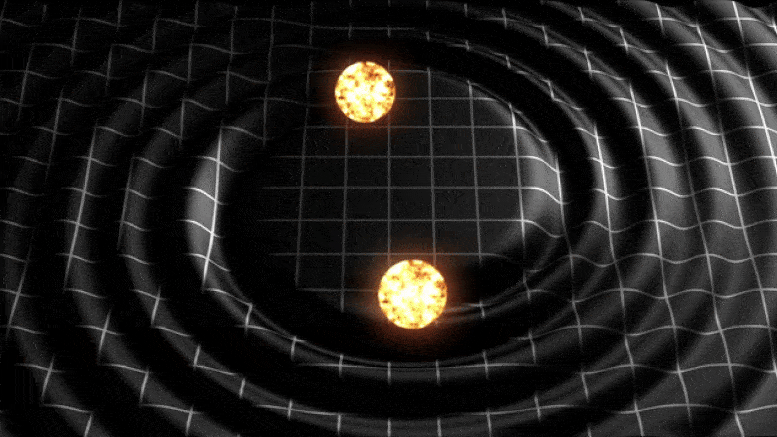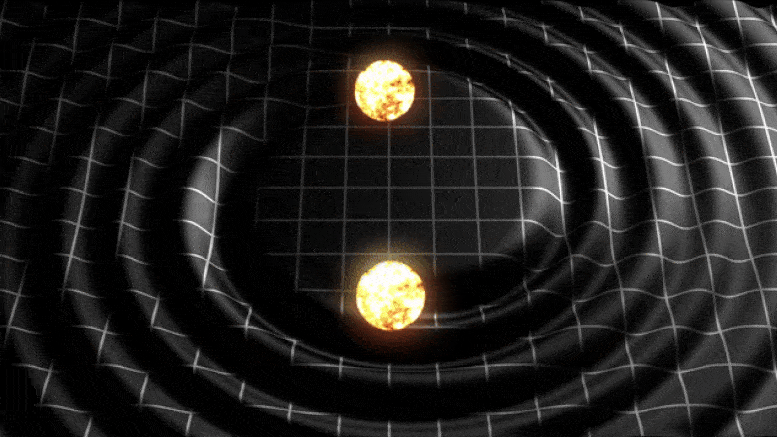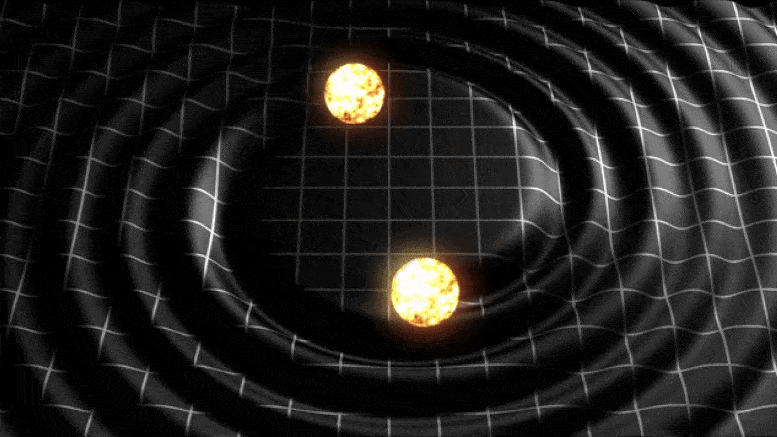
Animation illustrant les ondes gravitationnelles.
Les ondes gravitationnelles sont des ondulations de l’espace-temps créées par des objets astronomiques lointains et détectées par de grands détecteurs complexes (comme les détecteurs d’ondes gravitationnelles). LIGO, Virgoet KAGRA). La recherche de signaux d’ondes gravitationnelles dans les données des détecteurs est une tâche complexe qui nécessite des techniques avancées de traitement du signal et des ressources de supercalcul. En raison de cette complexité, il est difficile d’expliquer les recherches d’ondes gravitationnelles dans un laboratoire de premier cycle, notamment parce qu’une démonstration en direct à l’aide d’un détecteur d’ondes gravitationnelles ou d’un superordinateur n’est pas possible. Grâce à la simplification et à l’analogie, les démonstrations sur table sont efficaces pour expliquer ces recherches et ces techniques.
Une équipe de scientifiques d’OzGrav, issus de plusieurs institutions et disciplines, a conçu une démonstration sur table avec des exemples d’analyse de données pour expliquer les recherches d’ondes gravitationnelles et les techniques de traitement du signal. Cette démonstration, qui peut être utilisée comme outil d’enseignement dans les laboratoires de physique et d’ingénierie de premier cycle, sera publiée dans le bulletin d’information de la Commission européenne. American Journal of Physics.
L’auteur principal du projet James Gardner (qui était un étudiant de premier cycle d’OzGrav à l’Université de Melbourne pendant le projet et maintenant un chercheur de troisième cycle à l’Australian National University) explains: “This demonstration offers some charming insights into a live field of research that students like me should appreciate for its recency compared to the age of most ideas they encounter.”
Table-top gravitational-wave demonstrations
Gravitational wave detectors are very complicated and huge — laser light is sent down tubes kilometers long! But the workings of a gravitational-wave detector can be demonstrated using table-top equipment. Researchers at the University of Adelaide have developed AMIGO to do just that! Deeksha Beniwal, co-author of this study and an OzGrav PhD student at the University of Adelaide explains: “With AMIGO, the portable interferometer, we can easily share how LIGO uses the fundamental properties of light to detect ripples from the most distant reaches of the universe.”
This work expands on the portable interferometer demonstration with a selection of examples for students in both physics and electrical engineering. Changrong Liu, co-author of this study and an OzGrav PhD student in electrical engineering at the University of Melbourne, explains: “This project offers a great opportunity for electrical engineering students like me to put some of their knowledge into the real and exciting physical world.”
Explaining the hunt for continuous gravitational waves
To demonstrate searching for signals with the table-top set up, the team first needed to make some fake signals to find! This is where the analogy of sound comes in: audio signals are used to mimic gravitational waves interacting with the detector. The team focused on demonstrating the hunt for continuous gravitational waves, a type of gravitational wave that hasn’t been detected yet.
Hannah Middleton, co-author of the study and an OzGrav Associate Investigator (at the University of Birmingham), explains: “Continuous waves are long-lasting signals from spinning neutron stars. These signals should be present in the detector data all the time, but the challenge is to find them. This demonstration is directly inspired by the techniques developed by OzGrav physicists and electrical engineers in the hunt for continuous gravitational waves!“
A continuous wave signal can be slowly changing in frequency, so the audio signals used in this demonstration also change in frequency. ”We show, through using sound as an analogue to gravitational waves, what it takes to detect a wandering tone: a long signal that slowly changes pitch like whalesong,” explains Gardner.
Prof. Andrew Melatos, co-author of this study and leader of the OzGrav-Melbourne node explains: “We hope that undergraduate educators will emphasize the cross-disciplinary spirit of the project and use it as an opportunity to speak more broadly to students about careers at the intersection of physics and engineering. The future is very bright career-wise for students with experience in cross-disciplinary collaboration”
Written by OzGrav Assoc. Investigator Hannah Middleton (University of Birmingham) and OzGrav postgrad researcher James Gardner (ANU).
Reference: “Continuous gravitational waves in the lab: Recovering audio signals with a table-top optical microphone” by James W. Gardner, Hannah Middleton, Changrong Liu, Andrew Melatos, Robin Evans, William Moran, Deeksha Beniwal, Huy Tuong Cao, Craig Ingram, Daniel Brown and Sebastian Ng, 23 March 2022, American Journal of Physics.
DOI: 10.1119/10.0009409


