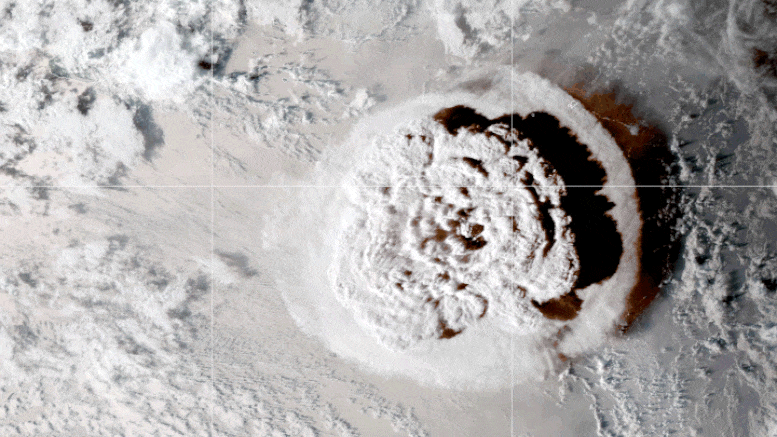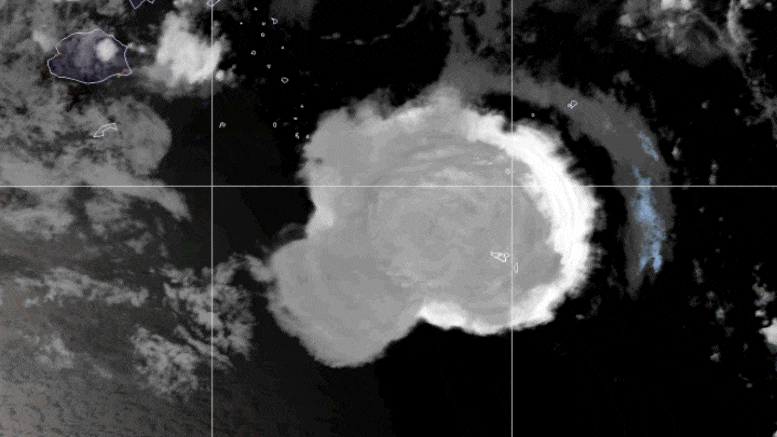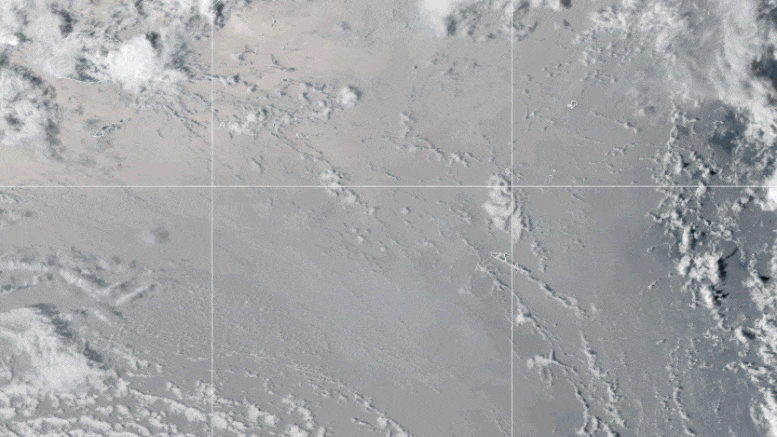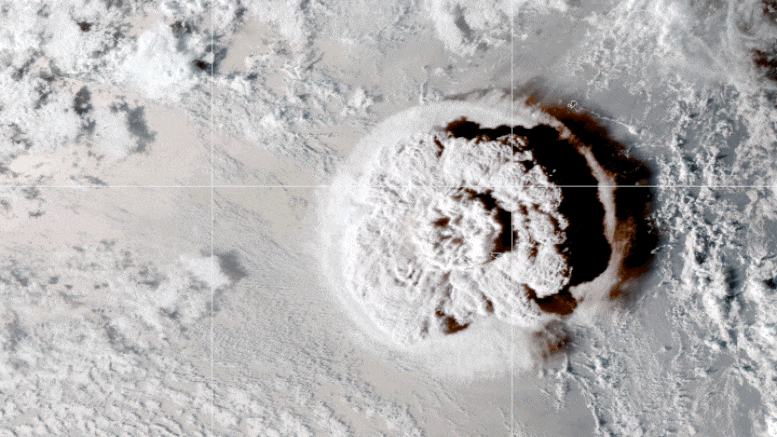
Cette vidéo en boucle montre une série d’images satellite GOES-17 qui ont capturé un nuage parapluie généré par l’éruption sous-marine du volcan Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai le 15 janvier 2022. Des ondes de choc en forme de croissant et de nombreux éclairs sont également visibles. Crédit : Image de l’observatoire terrestre de la NASA par Joshua Stevens à partir d’images GOES fournies par la NOAA et le NESDIS.
La NASA a détecté l’onde de choc de l’éruption sous-marine à haute altitude dans l’atmosphère.
La puissante éruption volcanique sous-marine qui a recouvert de cendres la nation insulaire des Tonga et envoyé des vagues de tsunami à travers le monde a également provoqué des ondulations dans l’ionosphère de la Terre, selon les mesures du Système mondial de positionnement différentiel (GDGPS) géré par ;” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{” attribute=””>NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
When the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano erupted on January 15, 2022, it unleashed a violent explosion with the equivalent force of 4 to 18 megatons of TNT, according to estimates from NASA geologist Jim Garvin. This explosion produced an acoustic shockwave that was strong enough to perturb the ionosphere, the outer layer of the atmosphere that starts about 50 to 56 miles (80 to 90 kilometers) above Earth’s surface and contains electrons ionized by the Sun’s energy.
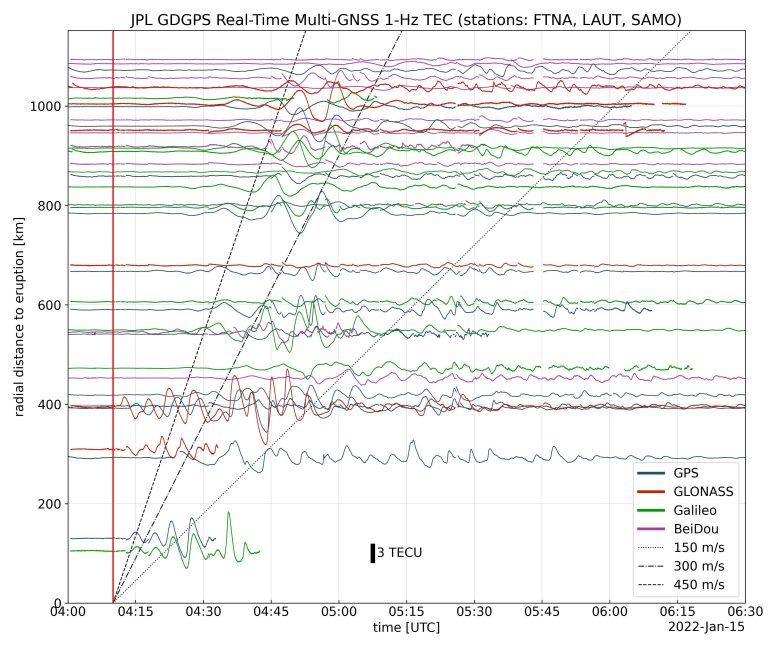
In the above image, the vertical red line in the data plot indicates the time of the eruption. The horizontal squiggles show electron density profiles over time, as recorded in the signals of four GNSS constellations, or groups of satellites: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou. The slanted dashed and dotted lines indicate the velocity of the waves. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/GDGPS
The eruption also caused a tsunami, which was enhanced by the atmospheric pressure waves of the explosion – a phenomenon known as a meteotsunami. The deformation of the ocean’s surface from these large waves further disturbed the ionosphere. The GDGPS observed ionospheric disturbances caused by the explosion and subsequent meteotsunami in real time. The system monitors the density of electrons in the ionosphere (measured as total electron content units, or TECU) by tracking the delay of global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) signals as they travel through the atmosphere.
GNSS data can serve an important role in contributing to tsunami early warning systems, shaving precious time off tsunami warnings when every second of advanced notice can save lives. The NASA Research Opportunities in Space and Earth Science (ROSES) A.37 project Local Tsunami Early Warning With GNSS Earthquake Source Products, funded by the Applied Sciences Disasters program area, is using this GNSS data to detect ground movement and model earthquake activity that could lead to tsunamis. The team is integrating this data into tsunami early warning systems operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Center for Tsunami Research (CTR).
NASA’s Space Geodesy Project also supports tsunami risk reduction through collaborations with the International GNSS Service, which manages the GNSS-enhanced Tsunami Early Warning Systems (GTEWS), the International Association of Geodesy’s Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS), and the Group on Earth Observations (GEO) Geodesy for the Sendai Framework Community Activity.
In the future, the ionospheric disturbance recorded by the GDGPS could also be integrated into these tsunami warning systems, increasing their effectiveness to warn communities and get people out of harm’s way before tsunami waves strike.