Un physico-chimiste et un groupe diversifié de ses étudiants travaillent sur les applications des diamants nanoscopiques.
Pour Abraham Wolcott, les diamants représentent bien plus que des pierres précieuses scintillantes et des symboles de statut social. Le physico-chimiste de l’université d’État de San Jose travaille sur les nanodiamants, qui sont des diamants microscopiques créés en brisant de plus gros diamants synthétiques. Les nanodiamants sont si petits qu’une rangée de 8 000 d’entre eux aurait la largeur d’un cheveu humain.
Que peut faire un scientifique comme M. Wolcott avec de si petites pierres précieuses ? En fait, pas mal de choses.
La matrice de carbone du diamant permet de l’utiliser en toute sécurité dans les cellules et les tissus vivants, qui sont principalement composés de carbone. Les diamants sont également chimiquement inertes, ils transportent bien la chaleur et sont optiquement transparents, ce qui signifie que la lumière les traverse facilement, selon M. Wolcott. En bref, leurs propriétés chimiques les rendent précieux pour une variété d’applications, allant de la détection en temps réel de la synthèse des protéines à quantum computing — while Wolcott adds that the technology is still in its early stages.
But there’s another thing that makes Wolcott’s research on nanodiamonds stand out: His lab is unique in that undergraduate and master’s students at San Jose State University (SJSU) do the bulk of the research, a task that is often reserved for more experienced investigators such as graduate students, post-doctoral researchers, and full-time lab technicians. “There’s no more exciting group of people to do research with than the students that I’ve had the pleasure to work with at San Jose State,” he says.

San Jose State University students Cynthia Melendrez, Camron Stokes, Jorge Lopez-Rosas and Tsz Megan Cheung were coauthors on a recent study of nanodiamonds that collected data at SSRL. Credit: Abraham Wolcott
A scientist’s best friend
Despite what you may have learned in high school chemistry about diamonds being pure carbon, Wolcott is more interested in what other elements are doing both inside and outside his nanodiamonds.
He says when nitrogen atoms get trapped within a diamond’s carbon lattice, this impurity creates an open spot, called the nitrogen vacancy center, where a carbon atom should be. When this center is hit with green light, it emits red light, and researchers can then rely on that glow to trace the nanodiamonds as they move throughout an organism, for example.
But whether they’re flowing through the bloodstream or a fiber optic cable, in order to get the diamonds to do what you want them to, “you need to be able to control their surface,” says Wolcott. “And that’s where my lab focuses most of its energy.”

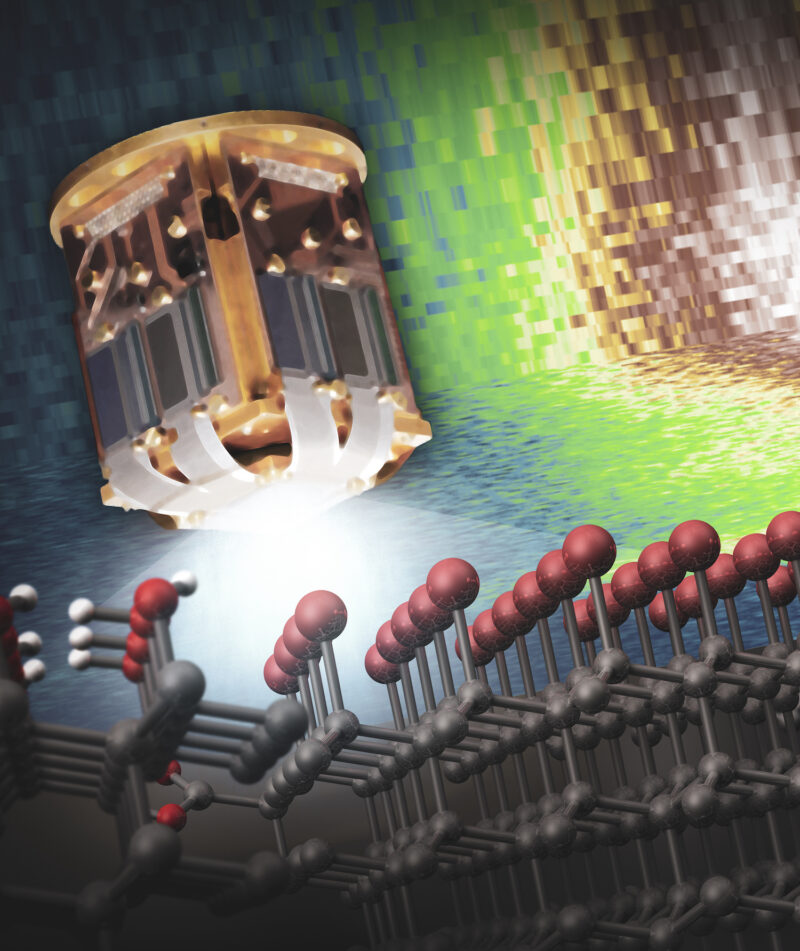
SSRL’s transition edge sensor (TES) helped the researchers study amines and other molecules arranged on the diamond lattice below. Wolcott’s group was among the first to try out the TES when it was put into service. Credit: Greg Stewart/SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
Wolcott’s research group in San Jose is working to attach different chemical groups to the surface of the nanodiamonds. Earlier this year, they published a paper in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters on developing a stable chemical reaction to attach nitrogen-containing chemical groups called amines to the surface of the nanodiamonds by first chemically coaxing bromine atoms onto the surface. The discoveries, which the researchers say could be useful for studying biological systems or in quantum sensors, are also being patented for their potential applications in nanotechnology.
This development was the product of lots of work, and Wolcott is quick to credit students like SJSU senior Tsz “Megan” Cheung, who has been in the lab since her freshman year. Cheung says she was initially interested in Wolcott’s lab because she had heard he allowed freshmen to join his group—and she really wanted to join a lab. Upon joining, she assumed she’d be washing dishes or restocking chemicals but was put to work on a research project almost right away. In fact, according to his students, jumping into experiments soon after joining is often the standard protocol in the Wolcott lab.
Cheung says some of her group’s chemical procedures can take up to five days to complete, which poses a potential logistical challenge since undergrads are generally busy with classes and aren’t expected to be in lab full-time. However, she says clear communication is key on the team. The students coordinate their schedules with one another and work through the reaction like a multi-day assembly line until the reaction is complete.
Nanodiamonds at the beamline
After trying to chemically attach different molecules to the surface of the nanodiamonds, Wolcott’s students need a way to test whether their reactions were successful. For this, they take their chemically-treated nanodiamonds to the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL) at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
The synchrotron acts as a “big factory to produce intense X-ray beams,” says staff engineer Sang-Jun Lee. As electrons hurtle through the synchrotron’s storage ring, super-strong magnets cause the beam of particles to wiggle, generating powerful X-rays that are funneled into experimental stations at each beamline. At Beam Line 10-1, an instrument called a transition edge sensor (TES) measures the X-rays coming out of the experimental sample with such fine resolution they can reveal the electronic structure of a substance – that is, patterns in the way its electrons are energetically arranged – says Lee. In the case of the nanodiamonds, TES can detect which chemical groups are present on the surface of the diamond.
Wolcott was among the first pilot users of TES when it was commissioned in 2016 – it was like the “science version of test-driving a Ferrari,” he recalls – and his students have been consistent users ever since, coming a few times a year, says Lee.

Wolcott’s students Tsz Megan Cheng, Camron X. Stokes, and Jorge Lopez-Rosas discuss their research at SSRL’s Beam Line 8-2. Credit: Abraham Wolcott
For many of Wolcott’s students, even just setting foot on SLAC’s campus is memorable. But they also get hands-on time at the beamline.
“It wasn’t that we were just shadowing and seeing other scientists do the chemistry,” says Cynthia Melendrez, a recent SJSU chemical engineering graduate and first author of the lab’s latest study. “It was incredible to be able to go into SSRL and actually do the experiments.”
Cheung agrees: “It’s hard to describe. You have to physically be there to feel the feeling of what a national lab is like.”
According to Lee, who has worked with Wolcott and his students at the beamline, learning the ropes isn’t easy for first-time users, and training undergraduates to use the beamline is especially rare. But, Lee says, Wolcott’s students have been able to do it – whether by writing programs to run the beamline automatically or by taking eight-hour-long night shifts to maximize the work they can get done during their long-awaited beamtime.
Camron Stokes, who recently graduated from SJSU with a degree in physics, was one of the students working the beamline’s graveyard shift. As a physics major, Stokes admits he was initially apprehensive about joining Wolcott’s chemistry lab.
But getting to work at SSRL was “like a dream come true,” he says. After getting a crash course in TES troubleshooting and working through the night to keep things running smoothly, he still got a sense of the magical feeling of being alone with TES at night. “I felt like it belonged to me,” he remembers. “It was really cool.”
‘You actually get a chance’
Stokes credits his confidence and sense of ownership over his research to Wolcott’s mentorship. “It’s not just that the research is good,” he says. “You actually get a chance.”
In recognition of his nanodiamond work, Stokes was recently given an award from the American Chemical Society’s Division of Colloids and Surface Science and will give an invited talk at the national meeting of the ACS in Chicago in August 2022.
Many people assume undergraduates don’t know enough or aren’t experienced enough to do research, says Meléndrez, who is now a science and engineering associate at SLAC’s LCLS. “But the leap of faith that Dr. Wolcott had [when I was] un étudiant de première année, c’était plutôt chouette.”
Wolcott note que de nombreux étudiants de la SJSU sont des étudiants universitaires de première génération et font face à une foule de circonstances de vie difficiles tout en continuant à soutenir leurs familles et à fréquenter l’école. Pour beaucoup d’entre eux, l’effort d’essayer de maintenir un programme de recherche unifié tout en jonglant avec les horaires des étudiants de premier cycle et ces défis supplémentaires pourrait ne pas en valoir la peine.
“Vous auriez pu diminuer les attentes et vous dire : “Vous savez quoi, je vais rendre le projet simple, parce que c’est ce qu’ils peuvent gérer”, dit Wolcott. “Je considérerais cela comme une pensée déficitaire”.
“Faire de la bonne science – de la vraie science – avec ces types de défis”, dit-il, “c’est vraiment ce qui fait sa spécificité”.
Le SSRL est un établissement utilisateur du DOE Office of Science.
Référence : “Metastable Brominated Nanodiamond Surface Enables Room Temperature and Catalysis-Free Amine Chemistry” par Cynthia Melendrez, Jorge A. Lopez-Rosas, Camron X. Stokes, Tsz Ching Cheung, Sang-Jun Lee, Charles James Titus, Jocelyn Valenzuela, Grace Jeanpierre, Halim Muhammad, Polo Tran, Perla Jasmine Sandoval, Tyanna Supreme, Virginia Altoe, Jan Vavra, Helena Raabova, Vaclav Vanek, Sami Sainio, William B. Doriese, Galen C. O’Neil, Daniel S. Swetz, Joel N. Ullom, Kent Irwin, Dennis Nordlund, Petr Cigler et Abraham Wolcott, 27 janvier 2022, The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c04090