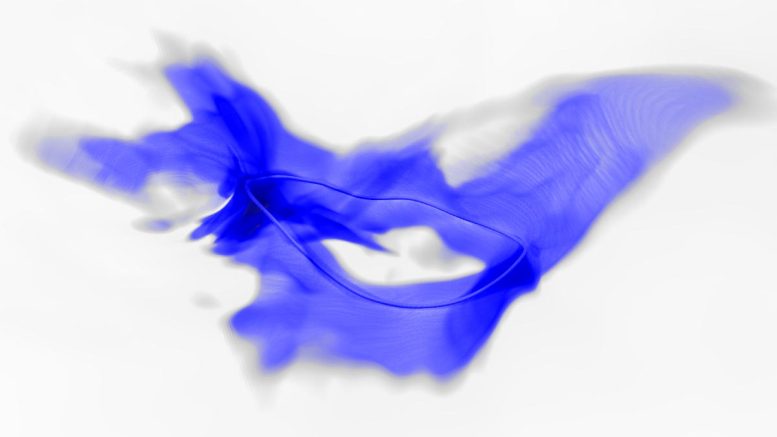
Dans une simulation de l’univers primitif, peu après le Big Bang, des cordes en forme de tornade (boucle bleu foncé) projettent des particules axions. Ces axions devraient être encore présents aujourd’hui et pourraient être la matière noire recherchée par les astrophysiciens. Crédit : Malte Buschmann, Université de Princeton
En utilisant un raffinement adaptatif du maillage, une simulation par supercalculateur réduit la gamme de masse des axions.
Les physiciens qui recherchent – sans succès – le candidat le plus favorisé aujourd’hui pour la matière noire, l’axion, ont cherché au mauvais endroit, selon une nouvelle simulation par supercalculateur de la façon dont les axions ont été produits peu après la Big Bang 13.6 billion years ago.
Using new calculational techniques and one of the world’s largest computers, Benjamin Safdi, assistant professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley; Malte Buschmann, a postdoctoral research associate at Princeton University; and colleagues at MIT and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory simulated the era when axions would have been produced, approximately a billionth of a billionth of a billionth of a second after the universe came into existence and after the epoch of cosmic inflation.
The simulation at Berkeley Lab’s National Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) found the axion’s mass to be more than twice as big as theorists and experimenters have thought: between 40 and 180 microelectron volts (micro-eV, or µeV), or about one 10-billionth the mass of the electron. There are indications, Safdi said, that the mass is close to 65 µeV. Since physicists began looking for the axion 40 years ago, estimates of the mass have ranged widely, from a few µeV to 500 µeV.
“We provide over a thousandfold improvement in the dynamic range of our axion simulations relative to prior work and clear up a 40-year old question regarding the axion mass and axion cosmology,” Safdi said.
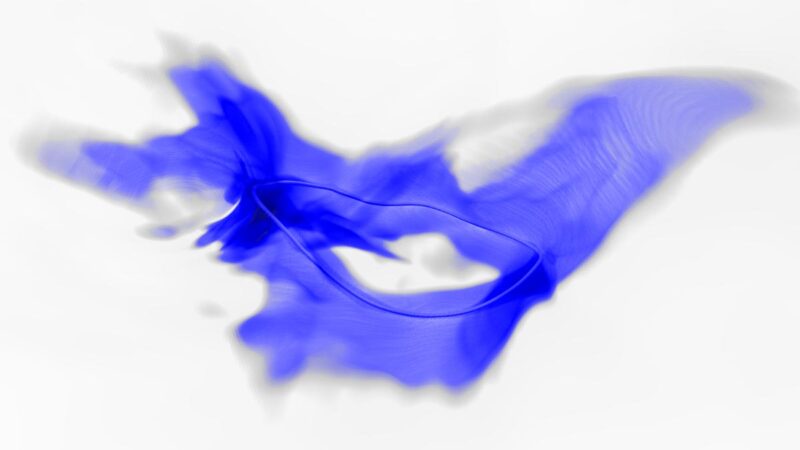
Un zoom sur une petite partie de la simulation par superordinateur de l’univers primitif montre la formation de défauts topologiques appelés cordes (jaune), qui se tordent et vibrent à des vitesses proches de celle de la lumière. Lorsque les cordes se tordent, vibrent et rétrécissent, elles émettent un rayonnement sous la forme d’axions (bleu). Ce rayonnement axion pourrait alors devenir la matière noire de notre univers. L’objectif de cette simulation est de mesurer précisément la quantité de rayonnement axion produit par le réseau de cordes qui se rétrécit, et de calculer à partir de là la masse attendue de la particule axion. Crédit : Malte Buschmann, Université de Princeton
La masse plus définitive signifie que le type d’expérience le plus courant pour détecter ces particules insaisissables – une chambre de résonance micro-onde contenant un champ magnétique puissant, dans laquelle les scientifiques espèrent capter la conversion d’un axion en une faible onde électromagnétique – ne pourra pas les détecter, quelles que soient les modifications apportées à l’expérience. La chambre devrait être plus petite que quelques centimètres de côté pour détecter l’onde à haute fréquence d’un axion de masse supérieure, a déclaré Safdi, et ce volume serait trop petit pour capturer suffisamment d’axions pour que le signal s’élève au-dessus du bruit.
“Notre travail fournit l’estimation la plus précise à ce jour de la masse de l’axion et indique une gamme spécifique de masses qui n’est pas actuellement explorée en laboratoire”, a-t-il déclaré. “Je pense vraiment qu’il est logique de concentrer les efforts expérimentaux sur les masses d’axion de 40 à 180 µeV, mais il y a beaucoup de travaux qui se préparent à s’attaquer à cette gamme de masses.”
Un type d’expérience plus récent, un plasma haloscope, which looks for axion excitations in a metamaterial — a solid-state plasma — should be sensitive to an axion particle of this mass, and could potentially detect one.
“The basic studies of these three-dimensional arrays of fine wires have worked out amazingly well, much better than we ever expected,” said Karl van Bibber, a UC Berkeley professor of nuclear engineering who is building a prototype of the plasma haloscope while also participating in a microwave cavity axion search called the HAYSTAC experiment. “Ben’s latest result is very exciting. If the post-inflation scenario is right, after four decades, discovery of the axion could be greatly accelerated.”
If axions really exist.
The work will be published today (February 25, 2022) in the journal Nature Communications.
Axion top candidate for dark matter
Dark matter is a mysterious substance that astronomers know exists — it affects the movements of every star and galaxy — but which interacts so weakly with the stuff of stars and galaxies that it has eluded detection. That doesn’t mean dark matter can’t be studied and even weighed. Astronomers know quite precisely how much dark matter exists in the Milky Way Galaxy and even in the entire universe: 85% of all matter in the cosmos.
To date, dark matter searches have focused on massive compact objects in the halo of our galaxy (called massive compact halo objects, or MACHOs), weakly interacting massive particles (WIMPs) and even unseen black holes. None turned up a likely candidate.
“Dark matter is most of the matter in the universe, and we have no idea what it is. One of the most outstanding questions in all of science is, ‘What is dark matter?’” Safdi said. “We suspect it is a new particle we don’t know about, and the axion could be that particle. It could be created in abundance in the Big Bang and be floating out there explaining observations that have been made in astrophysics.”
Though not strictly a WIMP, the axion also interacts weakly with normal matter. It passes easily through the earth without disruption. It was proposed in 1978 as a new elementary particle that could explain why the neutron’s spin does not precess or wobble in an electric field. The axion, according to theory, suppresses this precession in the neutron.
“Still to this day, the axion is the best idea we have about how to explain these weird observations about the neutron,” Safdi said.
In the 1980s, the axion began to be seen also as a candidate for dark matter, and the first attempts to detect axions were launched. Using the equations of the well-vetted theory of fundamental particle interactions, the so-called Standard Model, in addition to the theory of the Big Bang, the Standard Cosmological Model, it is possible to calculate the axion’s precise mass, but the equations are so difficult that to date we have only estimates, which have varied immensely. Since the mass is known so imprecisely, searches employing microwave cavities — essentially elaborate radio receivers — must tune through millions of frequency channels to try to find the one corresponding to the axion mass.
“With these axion experiments, they don’t know what station they’re supposed to be tuning to, so they have to scan over many different possibilities,” Safdi said.
Safdi and his team produced the most recent, though incorrect, axion mass estimate that experimentalists are currently targeting. But as they worked on improved simulations, they approached a team from Berkeley Lab that had developed a specialized code for a better simulation technique called adaptive mesh refinement. During simulations, a small part of the expanding universe is represented by a three-dimensional grid over which the equations are solved. In adaptive mesh refinement, the grid is made more detailed around areas of interest and less detailed around areas of space where nothing much happens. This concentrates computing power on the most important parts of the simulation.
The technique allowed Safdi’s simulation to see thousands of times more detail around the areas where axions are generated, allowing a more precise determination of the total number of axions produced and, given the total mass of dark matter in the universe, the axion mass. The simulation employed 69,632 physical computer processing unit (CPU) cores of the Cori supercomputer with nearly 100 terabytes of random access memory (RAM), making the simulation one of the largest dark matter simulations of any kind to date.
The simulation showed that after the inflationary epoch, little tornadoes, or vortices, form like ropey strings in the early universe and throw off axions like riders bucked from a bronco.
“You can think of these strings as composed of axions hugging the vortices while these strings whip around forming loops, connecting, undergoing a lot of violent dynamical processes during the expansion of our universe, and the axions hugging the sides of these strings are trying to hold on for the ride,” Safdi said. “But when something too violent happens, they just get thrown off and whip away from these strings. And those axions which get thrown off of the strings end up becoming the dark matter much later on.”
By keeping track of the axions that are whipped off, researchers are able to predict the amount of dark matter that was created.
Adaptive mesh refinement allowed the researchers to simulate the universe much longer than previous simulations and over a much bigger patch of the universe than previous simulations.
“We solve for the axion mass both in a more clever way and also by throwing just as much computing power as we could possibly find onto this problem,” Safdi said. “We could never simulate our entire universe because it’s too big. But we don’t need to stimulate our entire universe. We just need to simulate a big enough patch of the universe for a long enough period of time, such that we capture all of the dynamics that we know are contained within that box.”
The team is working with a new supercomputing cluster now being built at Berkeley Lab that will enable simulations that will provide an even more precise mass. Called Perlmutter, after Saul Perlmutter, a UC Berkeley and Berkeley Lab physicist who won the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics for discovering the accelerating expansion of the universe driven by so-called dark energy, the next-generation supercomputer will quadruple the computing power of NERSC.
“We want to make even bigger simulations at even higher resolution, which will allow us to shrink these error bars, hopefully down to the 10% level, so we can tell you a very precise number, like 65 plus or minus 2 micro-eV. That then really changes the game experimentally, because then it would become an easier experiment to verify or exclude the axion in such a narrow mass range,” Safdi said.
For van Bibber, who was not a member of Safdi’s simulation team, the new mass estimate tests the limits of microwave cavities, which work less well at high frequencies. So, while the lower limit of the mass range is still within the ability of the HAYSTAC experiment to detect, he is enthused about the plasma haloscope.
“Over the years, new theoretical understanding has loosened the constraints on the axion mass; it can be anywhere within 15 orders of magnitude, if you consider the possibility that axions formed before inflation. It’s become an insane task for experimentalists,” said van Bibber, who holds UC Berkeley’s Shankar Sastry Chair of Leadership and Innovation. “But a recent paper by Frank Wilczek’s Stockholm theory group may have resolved the conundrum in making a resonator which could be simultaneously both very large in volume and very high in frequency. An actual resonator for a real experiment is still some ways away, but this could be the way to go to get to Safdi’s predicted mass.”
Once simulations give an even more precise mass, the axion may, in fact, be easy to find.
“It was really crucial that we teamed up with this computer science team at Berkeley Lab,” Safdi said. “We really expanded beyond the physics field and actually made this a computing science problem.”
Reference: “Dark matter from axion strings with adaptive mesh refinement” 25 February 2022, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28669-y
Safdi’s colleagues include Malte Buschmann of Princeton; MIT postdoctoral fellow Joshua Foster; Anson Hook of the University of Maryland; and Adam Peterson, Don Willcox and Weiqun Zhang of Berkeley Lab’s Center for Computational Sciences and Engineering. The research was largely funded by the U.S. Department of Energy through the Exascale Computing Project (17-SC-20-SC) and through the Early Career program (DESC0019225).