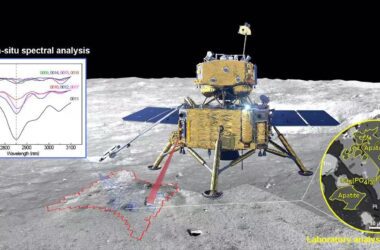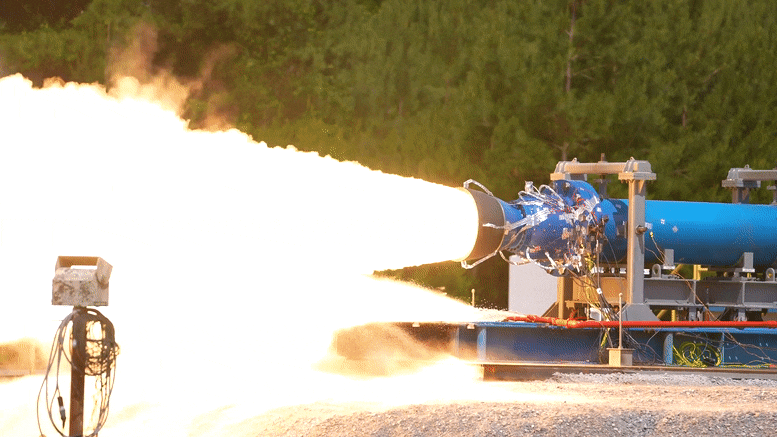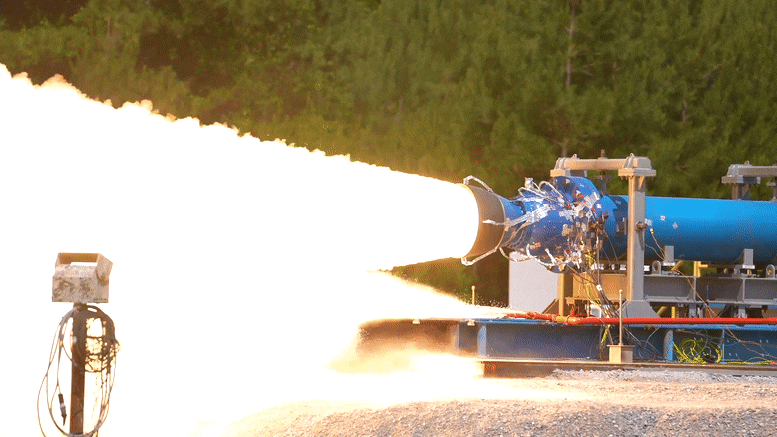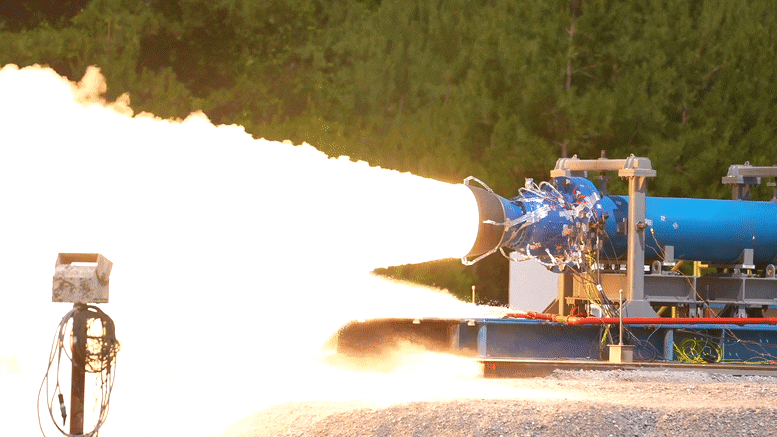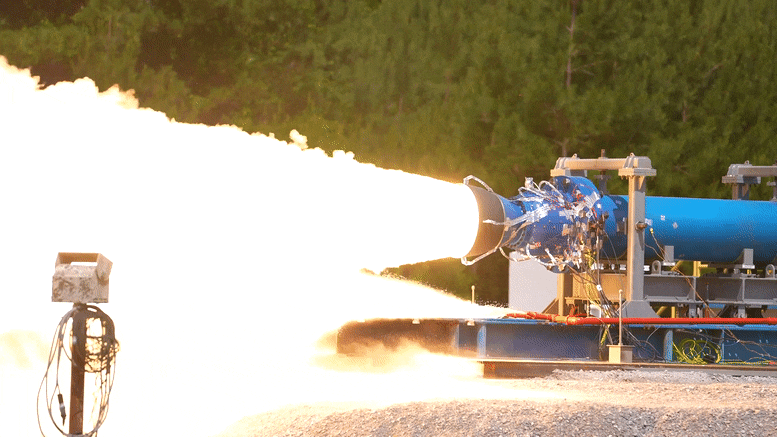
Le 1er juin 2022, les ingénieurs de la NASA ont réalisé avec succès un essai de moteur-fusée à propergol solide à petite échelle au Marshall Space Flight Center de la NASA à Huntsville, en Alabama.
Le Space Launch System (SLS) is NASA’s super heavy-lift expendable launch vehicle that has been in development since 2011. It will be capable of launching heavy payloads into orbit, as well as providing the foundation for human exploration beyond Earth’s orbit.
SLS is designed to be evolvable, so it can support a multitude of mission types in the future. These larger and more powerful versions of the SLS will require larger and more powerful boosters.
As part of this upgraded booster development, engineers successfully fired a 2-foot-diameter, subscale solid rocket booster on June 1, 2022, at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.
The test, conducted in Marshall’s East Test Area, produced 92,000 pounds of thrust and was done as part of the booster obsolescence and life extension (BOLE) program, providing an upgraded booster design for the evolved configuration of the Space Launch System rocket for Artemis IX and beyond. The BOLE booster will be a larger and more powerful solid rocket motor to make the SLS rocket capable of sending heavier payloads to the Moon and beyond.

NASA engineers successfully completed a subscale solid rocket motor test June 1, 2022, at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The subscale motor produced 92,000 pounds of thrust during the hot fire test. This was the second test supporting development efforts for a new motor design for Artemis missions after Artemis VIII. Credit: NASA/Samuel Lott
The test was the second in the series to evaluate the new motor design with an added half segment, a new propellant, a new aft dome design, and a new nozzle design. The first test was completed on December 2, 2021, and produced 76,400 pounds of thrust.
For this second test, lead booster contractor Northrop Grumman used a different propellant than in the first test to put the motor under the maximum expected operating pressure it could experience on launch day. Engineers will use data from the test to analyze how the motor performed under this pressure, which could be reached on a really hot day on the launch pad at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Les ingénieurs de la NASA ont réalisé avec succès un essai de moteur-fusée à poudre à petite échelle le 1er juin 2022, au Marshall Space Flight Center de la NASA à Huntsville, en Alabama. Le moteur à échelle réduite a produit une poussée de 92 000 livres au cours de l’essai à chaud. Il s’agissait du deuxième test appuyant les efforts de développement d’une nouvelle conception de moteur pour les missions Artemis après Artemis VIII. Crédit : NASA/Samuel Lott
Un troisième essai à petite échelle de la nouvelle conception, prévu pour l’année prochaine, évaluera des matériaux alternatifs pour la tuyère et l’isolation du moteur. Les tests du moteur à petite échelle sont une étape importante pour savoir comment le moteur BOLE se comportera à l’échelle réelle. L’équipe s’efforce d’achever la conception finale pour un test du moteur en grandeur réelle au printemps 2024 au centre d’essai de Northrop Grumman dans l’Utah.