Les personnes qui espèrent éviter l’un des pires effets secondaires du vieillissement – des douleurs osseuses, articulaires et musculaires qui ne disparaissent pas – pourraient avoir besoin de faire de l’exercice beaucoup plus fort et plus souvent qu’on ne le pensait auparavant.
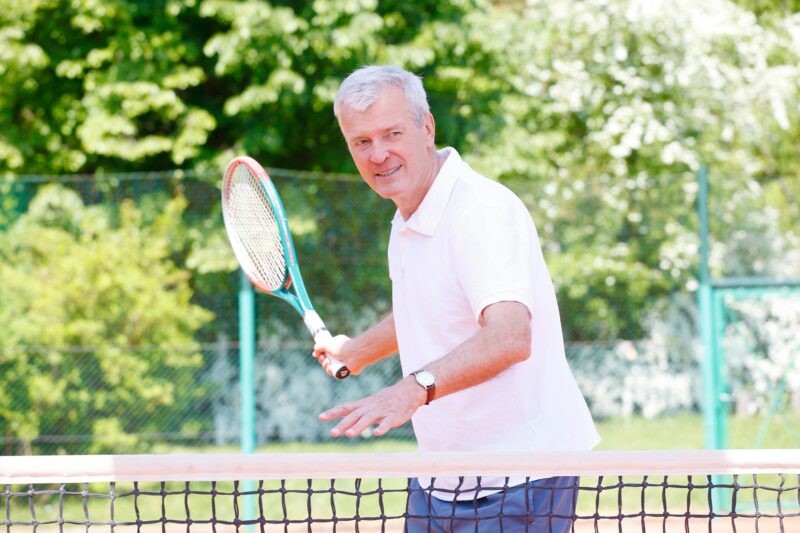
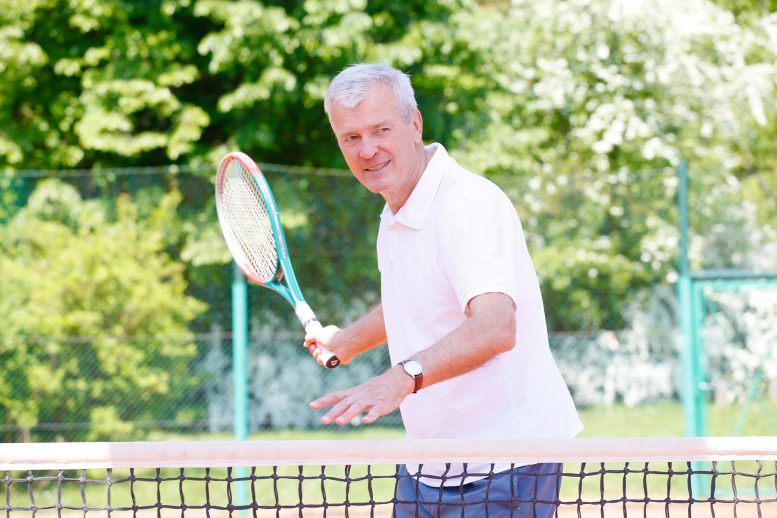
Selon une nouvelle étude, seul un niveau d’activité élevé au moins une fois par semaine – jouer au tennis, courir, nager, creuser avec une bêche ou faire un travail physique dur dans le cadre de son travail – semble aider à prévenir les douleurs musculo-squelettiques chroniques à long terme.
L’étude, dirigée par le Dr Nils Niederstrasser du University of Portsmouth, examined the data of 5,802 people aged 50 or more over ten years.
Nearly half – just over 2,400 – reported they suffered from musculoskeletal pain at the end of the ten-year period.
It’s well known that pain tends to be more common as we age, so it’s vital we look at what might help prevent and reduce it.
Dr. Niederstrasser said: “Chronic pain is a huge problem at any age, and one of the main causes for people calling in sick at work or visiting A&E. It is one of the most widespread and complex problems in the medical community and leads, for many who suffer with it, to a lower quality of life and poor wellbeing.
“It’s well known that pain tends to be more common as we age, so it’s vital we look at what might help prevent and reduce it.
“The lack of longitudinal studies among older adults of the risk factors for chronic pain is alarming.
“For many complex reasons, the solution to the problem of chronic pain in older people has proved elusive.”
The study is the first to examine the experience of chronic pain alongside gender, BMI, age, and wealth over a long time period.
Report co-author Dr. Nina Attridge, also at the University of Portsmouth, said all activity helped lower the chances of suffering pain but, over time, only high levels of physical activity appeared to lower the risk of someone developing musculoskeletal pain.
She said being poor, being female, and being overweight or obese were all found to independently be risk factors for suffering musculoskeletal pain.
She hopes the findings encourage those who design programs to help people avoid chronic pain to include regular vigorous physical activity, weight loss programs and find ways to address helping those on lower incomes.
For the study, moderate exercise included activities such as dancing, walking, stretching, and gardening.
Mild activity included activities such as doing laundry, vacuuming, and DIY.
Dr. Niederstrasser said: “Such activity – any activity – does help people stay well and feel better than not exercising, but mild exercise does not appear to have a long-term effect on the development of chronic pain.
“Activity needs to not only be vigorous, it needs to be done at least once a week.
“A person who cycles, for example, once a month and whose only other activity was light housework would still be classed as sedentary.”
The study found persistent pain was more common in women, possibly because of hormonal differences; in those who were obese or overweight, probably because extra weight adds a burden to the body’s joints; and in those who were less wealthy, possibly because higher disposable income may enable people to seek extra care, in addition to that covered by insurances or national health services, to treat ailments and injuries.
The study used data from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing.
It is published in PLOS ONE.
Reference: “Associations between pain and physical activity among older adults” by Nils Georg Niederstrasser and Nina Attridge, 28 January 2022, PLOS ONE.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263356